Knowledge
CAT Ratings Analysis: Safe Range of Use and Probe Design for Measurement Accessories
In electrical testing, the safety of the user is of paramount importance. In order to ensure safety, we need to understand the capabilities of the system we are dealing with and knowledge of the electrical system, and the appropriate technical knowledge is required when using electrical test equipment.
I. Purpose of the category rating system
The purpose of the category rating system is to protect the user from the unpredictable effects of high-energy impulses (transients) caused, for example, by grid or load faults. The risk to life and safety from these transients, such as lightning strikes, transients and surges, depends on the location within the power path where the test is performed. The category relates to the energy in the pulse, not just the peak voltage it reaches.
II. IEC 61010-031 standard
IEC 61010-031 (or the equivalent national product safety standard) defines three measurement categories, from CAT II to CAT IV. The higher the rating, the more stringent the safety requirements for the measurement accessories. In other words, the higher the CAT rating, the more energy the device must withstand and protect the user from transients. It is important to note that IEC 61010-031 only applies to low-voltage test equipment rated up to 1000V.
III. Measurement categories and examples
● CAT II
Purpose: Measurements on circuits directly connected to the socket of a low-voltage device.
Safety requirements: There shall be at least three levels of overcurrent protection between these circuits and the power transformer.
Example: Measurement of power nodes in household appliances, portable tools and similar equipment.
● CAT III
Purpose: Measurement of the distribution part of a building's low-voltage power supply units.
Safety requirements: There should be at least two levels of overcurrent protection between these points and the power transformer.
Examples: Measurements on distribution boards, circuit breakers, wiring (including cables, busbars, junction boxes, switches, sockets in fixtures), as well as on industrial and some other equipment (e.g. stationary motors permanently connected to fixtures).
● CAT IV
Purpose: Measurements at the source of low-voltage installations in buildings.
Safety requirements: There should be at least one level of overcurrent protection between these points and the power transformer.
Example: Measurements on electricity meters as well as primary overcurrent protection devices and ripple control units.
Unrated measurement category (CAT I)
Purpose: For measurements on circuits not directly connected to the mains supply.
Examples: Special protection (internal) circuits from power supplies, telephones, vehicle electrical installations.
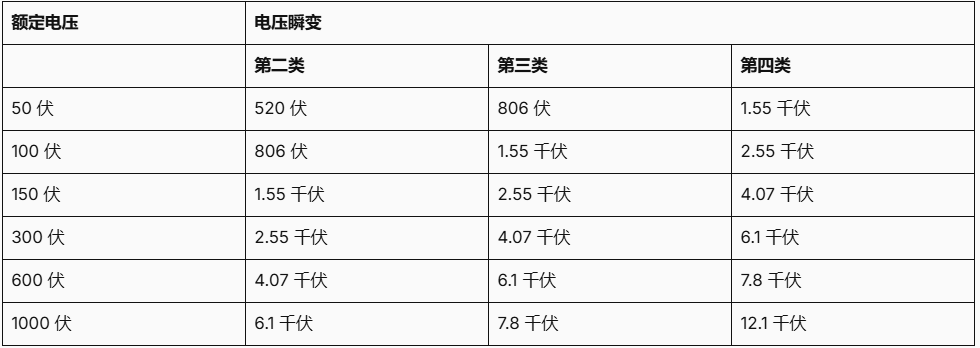
The table below shows that in each category there are predefined operating voltages of 50 V, 100 V, 150 V, 300 V, 600 V and 1000 V. The higher the voltage, the higher the operating voltage. The higher the voltage in a given category, the higher the required level of protection. For measurements below CAT II, no transient protection is recommended.
IV.Safe use of measuring accessories
● CAT rating markings:
All measuring accessories suitable for category-rated test circuits are marked with the CAT rating.
The CAT rating is used to indicate the safe use range of the probe or measurement accessory.
● Category ratings for active differential probes:
Active differential probes are clearly labeled with the category rating and its associated voltage rating in the probe and in the specifications.
A CAT II 1000V rated probe, for example, is not equivalent, even though its transient protection voltage is the same as a CAT III 600V rated probe.
Each probe is designed for a specific CAT rating and does not have a higher rating.
● Rated test product versus labeled ratings:
Some probes may have a rated test product that is higher than the marked rating on the probe, but this does not mean that they can be used at a higher CAT rating.
● Characteristics of CAT III products:
CAT III products are designed with higher insulation, creepage distances, and clearance distances to provide greater safety.